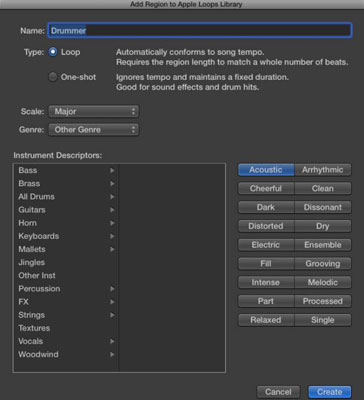
Com o Logic Pro X, você obtém um monte de instrumentos que podem facilmente substituir cada sintetizador e teclado que você possui. Eles são poderosos e flexíveis - e têm um som incrível. Além disso, os sintetizadores do Logic Pro podem parecer difíceis de programar quando você olha todos os controles e parâmetros que pode ajustar. Aqui, você faz um tour pelas interfaces e parâmetros do instrumento. Confira uma demonstração de vídeo mais detalhada do que esses sintetizadores Logic Pro podem fazer , onde você vê como os sintetizadores funcionam e como usar esses sintetizadores Logic Pro em sua música.
Para tocar os sintetizadores Logic Pro, você deve criar uma faixa de instrumento de software e selecionar o instrumento no slot de instrumento de faixa de canal da seguinte maneira:
Escolha Faixa → Nova faixa de instrumento de software (ou pressione Opção-⌘ -S).
Uma nova trilha de instrumento de software é adicionada à lista de trilhas.
Escolha Exibir → Mostrar Inspetor (ou pressione I).
O inspetor é aberto à esquerda da lista de trilhas.
Clique no lado direito do slot do instrumento e escolha o instrumento desejado.
A interface do instrumento de software é aberta.
Antes de começar o tour pela fabulosa coleção de sintetizadores do Logic Pro, é importante entender alguns termos básicos de síntese:
- Oscilador: um oscilador de sintetizador produz um sinal contínuo que forma a base do seu som. Os osciladores são capazes de produzir diversos formatos de onda com diferentes qualidades tonais. Os osciladores são a parte mais importante do sintetizador porque criam o som que os outros parâmetros do sintetizador irão moldar.
- Modulação: um som de sintetizador estático ganha interesse quando é variado de alguma forma. A modulação é o processo de variação dos parâmetros do sintetizador. Vibrato é um exemplo comum de modulação.
- Filtro: os sons sintetizados são moldados por meio do uso de filtros. Os filtros removem partes do espectro de frequência, permitindo que você contorne o som.
- Envelope: um envelope de sintetizador molda o início, o meio e o fim do seu som. O envelope mais comum ajusta o ataque, decadência, sustentação e liberação (ADSR). Por exemplo, um piano tem um ataque rápido, decadência rápida, sustentação média e liberação rápida.
- LFO: Um oscilador de baixa frequência (LFO) é um sinal, geralmente abaixo do espectro de frequência audível, que modula um sinal. LFOs são usados para alterar o sinal original de alguma forma. Um uso comum de um LFO é criar vibrato.
Logic Pro X: O sintetizador EFM1 FM
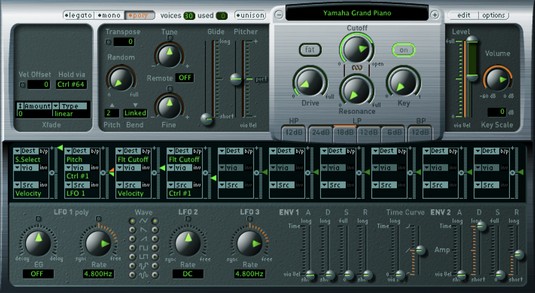
O sintetizador EFM1 FM obtém sons como o clássico Yamaha DX7 dos anos 80, um dos sintetizadores digitais mais populares de todos os tempos. O EFM1 usa síntese FM ( modulação de frequência ) para obter sons digitais como pianos elétricos, sinos, órgãos, baixos e outros sons complexos e legais. O EFM1 é capaz de reproduzir 16 vozes simultâneas e, ao contrário do DX7, é fácil de programar.

O sintetizador EFM1 FM.
Para criar sons com síntese FM, você define os parâmetros do modulador e da portadora e, a seguir, altera a intensidade do FM. As relações de afinação entre o modulador e a portadora definem os sobretons harmônicos. A intensidade do FM define o nível dos sobretons. Aqui está uma descrição dos parâmetros EFM1:
- Parâmetros do modulador: Os parâmetros do modulador estão no lado esquerdo da interface EFM1. Gire o botão Harmônico para definir a taxa de sintonia do sinal do modulador. Gire o botão de sintonia fina para ajustar os harmônicos. Gire o botão Wave totalmente para a esquerda para definir a forma de onda do modulador para a onda senoidal FM tradicional ou em qualquer lugar à direita para formas de onda adicionais. Gire o botão grande de FM central para ajustar a intensidade de FM.
- Parâmetros da operadora: Os parâmetros da operadora estão no lado direito da interface EFM1. Gire o botão Harmônico para definir a taxa de sintonia do sinal da portadora. Gire o botão de sintonia fina para ajustar os harmônicos. Clique no botão Fixed Carrier para evitar que a portadora seja modulada pelo teclado, pitch bend ou LFO.
- Parâmetros globais: na seção superior do EFM1, você pode definir os parâmetros globais. Clique no campo Transpor e no campo Tune para alterar a afinação do EFM1. Clique no campo Vozes para escolher quantas notas podem ser tocadas simultaneamente. Clique no campo Glide para definir o tempo que leva para deslizar de um pitch para outro, também conhecido como Clique no botão Unison para sobrepor vozes e tornar o som mais rico, o que também reduz pela metade o número de vozes que podem ser reproduzidas simultaneamente.
- Parâmetros de modulação: No centro do EFM1 estão os controles deslizantes do envelope de modulação que definem o ataque, decadência, sustentação e liberação (ADSR) do som. Gire o botão Modulator Pitch para definir como o envelope de modulação afeta o pitch. Gire o botão FM Depth para definir como o envelope de modulação afeta a intensidade do FM. Gire o botão giratório LFO para definir o quanto o LFO modula a intensidade de FM ou a afinação. Gire o botão Rate para definir a velocidade do LFO.
- Parâmetros de saída: A metade inferior do EFM1 é dedicada aos parâmetros de saída. Gire o botão Sub Osc Level para aumentar a resposta de graves. Gire o botão Stereo Detune para adicionar um efeito de coro ao som. Gire o botão Velocity para definir a sensibilidade da velocidade em resposta ao seu controlador MIDI. Gire o botão de nível principal para ajustar o volume geral. Ajuste os controles deslizantes do envelope de volume para definir o ADSR do som.
Clique no botão Randomize no canto inferior direito da interface EFM1 para criar sons aleatórios. Ajuste a quantidade de randomização clicando no campo Randomize e definindo a porcentagem de randomização. Se você gosta de sons digitais malucos, 100 por cento de randomização é seu melhor amigo.
Você não precisa ser um gênio da programação para obter ótimos sons dos sintetizadores do Logic Pro. Cada sintetizador vem com um menu de predefinições na parte superior da interface. Carregue um som de sua preferência, gire alguns botões e divirta-se. Abaixo do menu predefinido estão outros botões úteis, como Copiar, Colar, Desfazer e Refazer. O botão Comparar permite comparar suas configurações editadas com as configurações salvas para que você possa editar o quanto quiser, mas sempre volte ao ponto de partida.
Logic Pro X: O sintetizador subtrativo ES1
O sintetizador ES1 cria sons usando síntese subtrativa, na qual você começa com um oscilador e um sub-oscilador e, em seguida, subtrai partes do som para moldá-lo. O ES1 é modelado a partir de sintetizadores analógicos clássicos e é excelente para criar baixos, leads, pads e até sons de percussão.

The ES1 subtractive synth.
A description of the ES1 parameters follows:
- Oscillator parameters: The left half of the ES1 interface gives you the oscillator parameters that define your basic sound. Click the buttons on the left to choose the octave. Rotate the Wave knob to set the oscillator waveform. Rotate the Sub knob to set the suboscillator waveform. Adjust the Mix slider to set the mix between the two oscillators.
- Filter parameters: The center section of the ES1 filters the two oscillator waveforms. Adjust the Cutoff slider to set the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter. Adjust the Resonance slider to set the quality of the frequencies around the cutoff frequency. Click one of the four Slope buttons to choose how extreme the low-pass filter affects the signal. Adjust the Drive slider to affect the resonance setting and to overdrive the filter. Adjust the Key slider to set how the pitch adjusts the filter. Adjust the ADSR via Velocity slider to set how the filter is affected by note velocity.
- Amplifier parameters: The right sections of the ES1 adjust the volume level and performance. Adjust the Level via Velocity slider to set how the volume is affected by note velocity. Click the Amplifier Envelope buttons to set how the ADSR envelope affects the volume.
- Modulation parameters: The largest section of the dark-green area of the ES1 adjusts how the sound is modulated. The Glide parameter sets the speed of the portamento. Rotate the Wave and Rate knobs to set how the Low Frequency Oscillator (LFO) stimulates the sound over time. The Modulation Envelope sets how the modulation fades in or out. The Router parameters set the targets of the LFO and Modulation Envelope.
- Envelope parameters: The far right section of the dark-green area adjusts the ADSR envelope. Use the sliders to set the time of the attack, decay, sustain, and release (ADSR).
- Global parameters: The bottom row of parameters controls the ES1 global parameters. Click the Tune field to adjust the overall tuning. Click the Analog field to introduce random changes to the tuning and cutoff frequency, similar to an analog circuit that changes due to heat and age. Click the Bender Range to adjust the amount of pitch bend. Click the Out Level to adjust the overall volume. Click the Voices field to set the number of voices the ES1 can play simultaneously. Click the Chorus field to choose the type of built-in chorus effect that will thicken the sound.
The ES1 is a great instrument to use for getting the feel of analog synthesis. Many of the synths that follow have similar parameters. Getting the hang of setting oscillator waveforms, filters, envelopes, and modulators will help you take command of the synths and design your own sounds.
Some of these software instruments haven’t had their interfaces updated since Apple introduced hardware Retina displays, which are capable of extremely smooth and crisp graphics. The consequence is fuzzy graphics with controls and text that can be difficult to read. At the top right of the software instrument is a View pop-up menu that can change the size of the window. If you’re having trouble seeing something, make the window bigger.
Logic Pro X: The ES2 hybrid synth
The ES2 is like a combined EFM1 and ES1 synth plus another type of synthesis called wavetable synthesis. A wavetable is made up of many different waveforms that evolve from one to another or blend at once, creating complex digital sounds. Although the ES2 can produce sounds similar to the EFM1 and ES1, it shines at creating pads, sonic textures, and synthetic sounds that evolve over time.

The ES2 hybrid synth.
Check out the the unique features of the ES2:
- Oscillator parameters: The three numbered oscillators on the upper-left side of the ES2 interface choose the basic sound. The triangle-shaped area to the right of the three oscillators blends them together.
- Filter parameters: The round section in the center of the ES2 adjusts the filters that shape your synth sound.
- Amplifier parameters: The top-right section contains the ES2 volume level. You can add a sine wave to the output section using the Sine Level knob.
- Effects parameters: To the right of the ES2 parameters are several built-in effects, including distortion and chorus, as well as a flanger and a phaser.
- Planar pad: The X/Y pad to the right of the amplifier parameters can control two parameters simultaneously. The planar pad parameters are chosen in the modulation router or vector envelope.
- Modulation router and vector envelope parameters: The dark-blue strip of the ES2 controls the modulation sources and targets as well as the vector envelope generator. You can toggle between the modulation router and vector envelope using the Router and Vector buttons on the right.
- Modulation parameters: Below the modulation router and vector envelope parameters are the modulation parameters. Adjust the two LFOs and three envelopes to modulate the ES2 modulation targets. You set the modulation sources and targets in the modulation router.
- Macro controls and controller assignment parameters: The bottom strip of buttons and knobs are where you set the macro controls and MIDI controller assignments. Click the Macro or MIDI button to toggle between the two types of controls. Click the Macro Only button to hide all ES2 parameters except the preprogrammed macro controls, which are useful when you went to adjust the ES2 sounds globally. The MIDI controller assignments allow you to map controls on your MIDI controller to parameters of the ES2.
- Global parameters: Found above the filter parameters and to the left of the oscillator parameters are the ES2 global parameters. You can tune the instrument, set the number of voices, adjust the portamento speed, and more.
The ES2 hybrid synth can be used in surround mode to pan your sound throughout the surround spectrum if you’re monitoring your Logic Pro project in surround sound. Logic Pro designers have seemingly thought of everything. To get to the surround parameters, click the disclosure triangle at the bottom of the ES2 interface to display the advanced parameters.
Logic Pro X: The ES E ensemble synth
The ES E synth is a lightweight, eight-voice subtractive synth. The E in its name stands for ensemble, and the ES E is great for warm pads such as analog brass and strings. Best of all, it’s much easier to program than the ES1 or ES2.

The ES E ensemble synth.
Here’s a description of the ES E parameters:
- Oscillator parameters: The left side of the ES E interface adjusts the oscillator parameters. Click the buttons on the far left to choose the octave of your sound. Rotate the Wave knob all the way to the left to generate a sawtooth wave, which is bright with strong odd and even harmonics and excels at generating rich pads. The rest of the wave range generates pulse waves, which are hollow sounding with strong odd harmonics and can create excellent reedy sounds such as woodwinds.
- LFO parameters: The knobs below the wave parameter adjust the LFO settings. The LFO modulates the oscillator waveform. Rotate the Vibrato/PWM (pulse wave modulation) knob to set the modulation intensity. Rotate the Speed knob to set the LFO speed.
- Filter parameters: To the right of the oscillator and LFO parameters are the low-pass filter parameters. A low-pass filter allows low frequencies to pass through while reducing the higher frequencies. Rotate the Cutoff knob to set the cutoff frequency, and rotate the Resonance knob to raise or lower the frequencies around the cutoff frequency. Rotate the Attack/Release Intensity knob to adjust how the envelope generator affects the filter. Rotate the Velocity Filter knob to adjust how velocity affects the filter.
- Envelope parameters: To the right of the filter parameters are the envelope parameters. Adjust the Attack and Release sliders to set the level of your sound over time. A low attack setting will result in a more immediate sound, and a higher setting will result in a slow fade up to the final volume. A high release setting will cause the sound to slowly fade when you release the key, and a lower setting will cause the sound to fade quickly.
- Output parameters: To the right of the envelope parameters are the output parameters. Rotate the Volume knob to adjust the overall ESE volume. Rotate the Velocity Volume knob to adjust the velocity sensitivity.
- Effects parameters: To the right of the envelope parameters, you can choose a built-in effect. Choose between Chorus I, Chorus II, and Ensemble to thicken your sound.
Logic Pro X: The ES M mono synth
The ES M is another lightweight subtractive synth. The M stands for mono, which means the ES M can play only one note at a time. Monophonic synths such as the ES M are perfect for bass and lead sounds. Like the ES E, the ES M is simple to program and features a stripped-down set of controls. Both the ES E and ES M are great instruments for learning the basics of synthesis.

The ES M monophonic synth.
A description of the ES M parameters follows:
- Oscillator parameters: The left side of the ES M adjusts the oscillator parameters. Click the numbered buttons on the far left to choose the octave. Rotate the Mix knob all the way to the left to select a sawtooth wave and all the way to the right to select a rectangular wave. Rotate the Mix knob between the two positions to mix the sawtooth and rectangular waves. Rectangular waves, like pulse waves, are reedy and nasal and great for synth bass sounds. Rotate the Glide knob to adjust the speed of the portamento.
- Filter parameters: To the right of the oscillator parameters are the filter parameters. Rotate the Cutoff knob to adjust the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter. Rotate the Resonance knob to boost or cut the frequencies around the cutoff frequency. Rotate the Filter Intensity knob to adjust how the envelope generator modulates the cutoff frequency. Rotate the Filter Decay knob to adjust the filter envelope decay time. Rotate the Filter Velocity knob to adjust how velocity affects the filter.
- Volume parameters: To the lower right of the filter parameters are the output parameters. Rotate the Volume knob to adjust the overall volume. Rotate the Volume Decay knob to adjust how the sound decays over time. Rotate the Volume Velocity knob to adjust how volume responds to velocity. Rotate the Overdrive knob to add distortion to your sound.
Click the disclosure triangle at the bottom of the interface to view the extended parameters. You can adjust the pitch bend amount and fine-tuning in this area.
Logic Pro X: The ES P poly synth
The ES P is another lightweight subtractive synth. The P stands for polyphonic; you can play eight voices at once. The ES P is modeled after classic 80s synths and does a great job of creating analog pads, bass, and brass sounds.

The ES P polyphonic synth.
Here’s a description of the ES P parameters:
- Oscillator parameters: The left side of the ES P adjusts the oscillator parameters. Click the numbered buttons to choose the octave. The Oscillator sliders are used to mix the six oscillators. From left to right, you can set the level of a triangle wave, sawtooth wave, rectangle wave, suboscillator -1 (one octave below), suboscillator -2 (two octaves below), and noise generator.
- LFO parameters: To the right of the oscillator parameters are the LFO parameters. Rotate the Vibrato/Wah knob to adjust the amount of vibrato or wah-wah effect. Rotate the Speed knob to adjust the speed of the vibrato or wah.
- Filter parameters: To the right of the LFO parameters are the filter parameters. Rotate the Frequency knob to set the cutoff frequency of the low-pass filter. Rotate the Resonance knob to boost or cut the frequencies around the cutoff frequency. Click the 1/3, 2/3, or 3/3 buttons to adjust how the pitch affects the cutoff frequency modulation. Rotate the ADSR Intensity knob to adjust how the envelope generator affects the cutoff frequency modulation. Rotate the Velocity Filter knob to set how velocity affects the filter.
- Parâmetros de volume: no canto inferior direito dos parâmetros do filtro estão os parâmetros de volume. Gire o botão Volume para ajustar o volume geral. Gire o botão Velocity Volume para ajustar como a velocidade afeta o volume. Os níveis mais baixos imitam sintetizadores clássicos sem teclados sensíveis à velocidade; níveis mais altos tornam as notas mais altas se a tecla for tocada com mais força.
- Parâmetros de envelope: À direita dos parâmetros de volume estão os parâmetros de envelope. Ajuste os parâmetros de ataque, decadência, sustentação e liberação (ADSR) para ajustar o envelope ES P.
- Parâmetros de efeitos: À direita dos parâmetros de envelope estão os parâmetros de efeitos. Gire o botão Chorus para a direita para adicionar coro e engrossar seu som. Gire o botão Overdrive para a direita para adicionar distorção.
Logic Pro X: o vocoder de sintetizador EVOC 20
O EVOC 20 poly synth é um vocoder e um sintetizador de 20 vozes. Um vocoder (codificador de voz) pega um sinal de áudio de entrada, normalmente uma voz, e aplica esse sinal ao sintetizador, criando um sintetizador vocal híbrido. No entanto, uma voz não é a única coisa que você pode usar como entrada. Você pode inserir um loop de bateria ou um instrumento no sintetizador ou executar o sintetizador sem qualquer entrada como um sintetizador independente.

O EVOC 20 vocoder synth.
Para usar o EVOC 20 PS como um vocoder clássico, faça o seguinte:
No menu Side Chain no cabeçalho do plug-in EVOC 20 PS, escolha a fonte de entrada.
A fonte pode ser uma entrada ao vivo, uma trilha de áudio ou um barramento. O efeito de vocoder clássico usa uma entrada ao vivo ou uma trilha de vocal pré-gravada.
Silencie a fonte de entrada para que você ouça apenas a saída do EVOC 20 PS.
Toque seu controlador MIDI simultaneamente com a fonte de entrada.
O EVOC 20 PS sintetiza sua fonte de entrada.
Aqui está uma breve descrição de alguns parâmetros importantes do EVOC 20 PS:
- Parâmetros de análise da cadeia lateral: A área superior esquerda do EVOC 20 PS ajusta os parâmetros da cadeia lateral. Gire o botão Attack para definir o quão rápido ou lento o sintetizador reage ao início do sinal de entrada. Gire o botão Release para ajustar a rapidez ou lentidão com que o sintetizador reage ao final do sinal de entrada. Clique no botão Congelar para reter o sinal de entrada atual indefinidamente.
- Parâmetros de detecção U / V: O lado direito do EVOC 20 PS ajusta os parâmetros de detecção U / V (sem voz / voz). A voz humana é composta de sons vocalizados, como vogais, e sons surdos, como plosivas, fricativas e nasais. Gire o botão de sensibilidade para ajustar a sensibilidade do EVOC 20 PS aos sinais de entrada sonoros e não sonoros. Clique no campo Modo para escolher como os sons surdos são sintetizados. Gire o botão de nível para ajustar o volume do conteúdo sem voz.
Você obterá ótimos resultados se sua fonte de entrada for um volume constante com muito conteúdo de alta frequência. Certifique-se de que o volume da fonte de entrada não varia muito. Você também pode equalizar a fonte de entrada para aumentar o conteúdo de alta frequência.