Apa Itu Diri Dalam Python: Contoh Dunia Sebenar

Apa Itu Diri Dalam Python: Contoh Dunia Sebenar
Memotong nombor titik terapung dalam Python ialah operasi biasa yang dihadapi oleh ramai pengaturcara dalam pelbagai aplikasi. Proses ini melibatkan pengalihan tempat perpuluhan apungan, hanya meninggalkan bahagian integer. Ia merupakan teknik yang berharga untuk memudahkan pengiraan, meningkatkan kebolehbacaan dalam output dan mengurangkan kemungkinan ralat pembundaran.
Untuk memotong nilai apungan dalam Python, anda boleh menggunakan fungsi math.trunc(), modul perpuluhan atau manipulasi rentetan. Dengan menggunakan teknik ini, pembangun Python boleh menyesuaikan proses pemotongan mengikut keperluan khusus mereka dengan fleksibiliti dan ketepatan.

Dalam artikel ini, kita akan meneroka cara pemotongan boleh digunakan dalam pengaturcaraan Python untuk mencipta kod yang lebih cekap dan diperkemas . Kami akan menyelidiki pelbagai contoh praktikal, mengemukakan pandangan menyeluruh tentang cara menggunakan teknik ini untuk kesan maksimum.
Mari kita mulakan dengan melihat konsep dan teknik asas untuk memotong rentetan, nombor dan struktur data dalam Python.
Isi kandungan
Asas Python Truncate
Dalam bahagian ini, kita akan merangkumi definisi pemangkasan, lihat fungsi Python untuk pemangkasan, dan pelajari cara memotong tempat perpuluhan dan terapung.
1. Definisi Truncate dalam Python
Truncate ialah proses memendekkan nombor dengan membuang tempat perpuluhan. Ia merupakan konsep penting dalam sains komputer dan matematik dan digunakan untuk mengurangkan digit kepada bentuk yang lebih mudah tanpa mengubah nilainya.
2. Cara Menggunakan Fungsi Python Truncate
Terdapat beberapa cara untuk memotong nilai mutlak dalam Python. Satu kaedah biasa untuk mencapai pemangkasan adalah dengan menggunakan fungsi math.trunc() , yang secara langsung mengalih keluar tempat perpuluhan daripada nilai titik terapung binari.
Berikut ialah contoh:
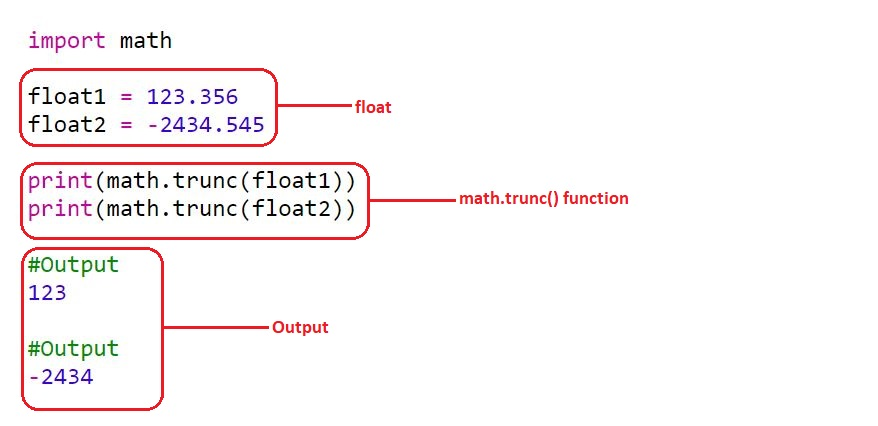
import math
float1 = 123.356
float2 = -2434.545
print(math.trunc(float1))
print(math.trunc(float2))
Pengeluaran:
123
-2434Kaedah ini memberikan hasil yang serupa kepada fungsi int() , yang juga memotong nombor yang diberikan dengan mengalih keluar tempat perpuluhan.
3. Cara Memotong Tempat Perpuluhan dan Terapung dalam Python
Dalam sesetengah kes, anda mungkin dikehendaki memotong apungan kepada bilangan digit perpuluhan tertentu. Fungsi round() boleh digunakan untuk membundarkan nombor dalam kes sedemikian. Walau bagaimanapun, sila ambil perhatian bahawa fungsi round() hanya membundarkan nombor dan bukannya memotongnya.
Jika anda ingin memotong ke titik perpuluhan tertentu, anda boleh menggunakan pendekatan berikut:
def truncate_float(float_number, decimal_places):
multiplier = 10 ** decimal_places
return int(float_number * multiplier) / multiplier
float3 = 3.14159
result = truncate_float(float3, 2)
print(result)
Pengeluaran:
3.14
Dalam contoh di atas, fungsi truncate_float() mengambil dua parameter — nombor apungan untuk dipotong dan bilangan titik perpuluhan yang dikehendaki.
Ia menggunakan pengganda untuk mengalihkan titik perpuluhan apungan terlebih dahulu, kemudian menukar hasilnya kepada integer (memotong nombor dengan berkesan), dan akhirnya membahagikan integer dengan pengganda untuk memulihkan titik perpuluhan kepada kedudukan asalnya.
Perlu diingat bahawa bekerja dengan terapung dalam Python boleh menyebabkan beberapa ketidaktepatan dalam pengiraan disebabkan sifat aritmetik titik terapung. Oleh itu, apabila ketepatan dan ketepatan adalah penting, pertimbangkan untuk menggunakan modul perpuluhan .
Baiklah, itulah asas cara memotong nilai dalam Python. Dalam bahagian seterusnya, kita akan melihat bagaimana anda boleh memotong nilai menggunakan perpustakaan matematik dan fungsi Python yang lain.
Memotong dalam Python Menggunakan Perpustakaan dan Fungsi Matematik
Dalam bidang pengaturcaraan Python, pengoptimuman selalunya penting. Menggunakan perpustakaan 'matematik' Python dan fungsi terbina dalamnya boleh meningkatkan prestasi dengan ketara, terutamanya apabila berurusan dengan set data yang besar atau pengiraan yang kompleks.
Bahagian ini dikhaskan untuk meneroka cara kami boleh menggunakan perpustakaan 'matematik' dan fungsi teguhnya untuk tugas pemangkasan — mengurangkan atau mengehadkan saiz data dengan cekap — dalam Python.
1. math.trunc()
Pustaka matematik Python menyediakan beberapa fungsi untuk berfungsi dengan nilai apungan, salah satunya ialah math.trunc() . Fungsi ini mengembalikan nilai terpotong apungan yang diberikan, dengan berkesan mengalih keluar bahagian pecahannya dan hanya meninggalkan bahagian integer.
Berikut ialah contoh cara menggunakan math.trunc() :
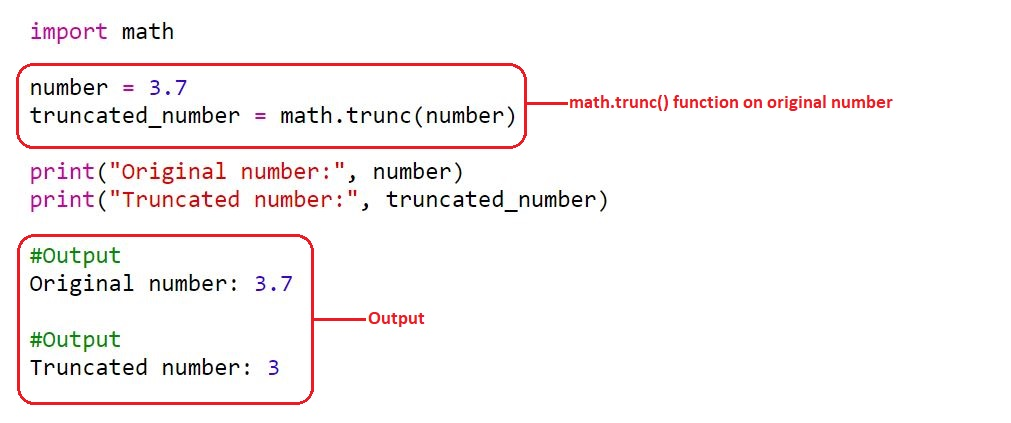
import math
number = 3.7
truncated_number = math.trunc(number)
print("Original number:", number)
print("Truncated number:", truncated_number)
Pengeluaran:
3
3.7math.trunc() membundarkan nombor ke arah sifar. Untuk nombor positif, ia berfungsi seperti fungsi lantai, dan untuk nombor negatif, ia berfungsi seperti fungsi siling.
2. math.floor() dan math.ceil()
Selain math.trunc() , perpustakaan matematik juga menyediakan fungsi untuk membundarkan nombor dalam cara yang berbeza, seperti fungsi math.floor() dan math.ceil() .
Fungsi math.floor () membundarkan nilai titik terapung ke bawah kepada integer terdekat, manakala math.ceil() membulatkan ke atas kepada integer terdekat.
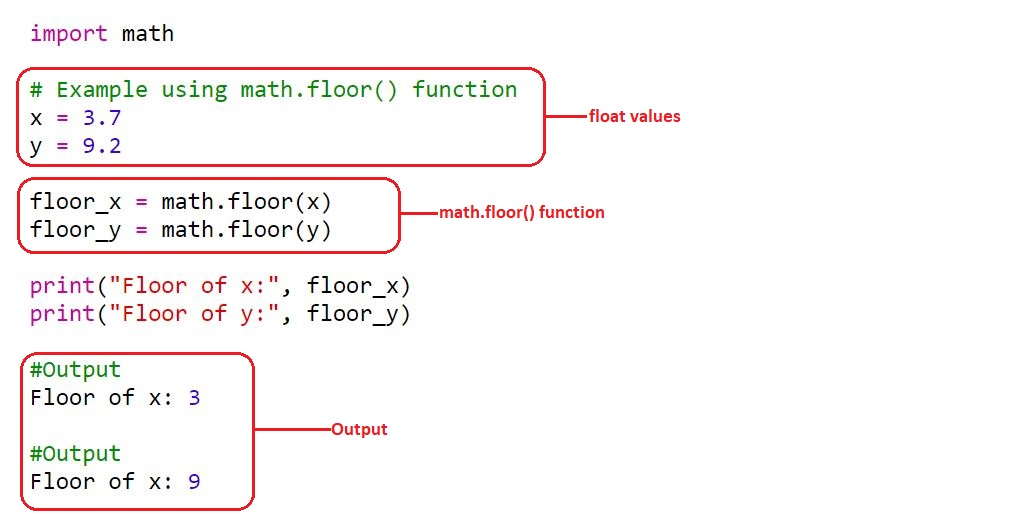
import math
# Example using math.floor() function
x = 3.7
y = 9.2
floor_x = math.floor(x)
floor_y = math.floor(y)
print("Floor of x:", floor_x)
print("Floor of y:", floor_y) Pengeluaran:
Floor of x: 3
Floor of y: 9Berikut ialah ilustrasi fungsi math.floor().
Coretan kod ini menunjukkan penggunaan fungsi math.ceil() :
import math
# Example usage of math.ceil()
x = 3.7
y = 9.2
z = -4.5
ceil_x = math.ceil(x)
ceil_y = math.ceil(y)
ceil_z = math.ceil(z)
# Output the results
print("Ceiling of", x, "is", ceil_x)
print("Ceiling of", y, "is", ceil_y)
print("Ceiling of", z, "is", ceil_z)
Pengeluaran:
Ceiling of 3.7 is 4
Ceiling of 9.2 is 10
Ceiling of -4.5 is -4
3. Floating Value Conversion Using int()
Another way to truncate a float value is by using the built-in int() function. When passed in a float, it’ll convert it to an integer by truncating the decimal part.
This approach can be more convenient for simple truncation cases, as it does not require importing the math library.
float5 = 7.65
float6 = -3.14
print(int(float5))
print(int(float6))
Output:
7
-3However, it’s essential to remember that the int() function is not equivalent to math.floor() or math.ceil(), as it only truncates the number without considering its sign.
Here’s the illustration of the above int() function for a float truncation in a code editor;

In summary, the Python math library offers multiple functions to work with float values, including truncating, rounding down, and rounding up. The math library is an essential tool to rely on when you need to perform advanced mathematical operations.
While the int() and math.trunc() functions offer simple ways to truncate floating-point values, the decimal module provides a more powerful and precise approach, so let’s explore that in the next section.
How to Truncate Values in Python With the Decimal Module
Python’s ‘decimal’ module is a powerful tool that offers precision handling of decimal numbers, a feature that comes in particularly handy when truncation is needed.
This section dives into the practical applications of this module for truncating values in Python. We’ll explore step-by-step examples and provide an in-depth understanding of the concepts behind this effective and precise data manipulation technique.
1. Using the Quantize Method
The quantize method of the Decimal class is a versatile tool for truncating decimal instances. This method allows developers to set the desired precision and rounding mode, ensuring accurate truncation.
Consider the following example:
from decimal import Decimal, ROUND_DOWN
number = Decimal('3.14159')
truncated = number.quantize(Decimal('1.'), rounding=ROUND_DOWN) print(truncated)Output:
3In this example, the quantize method is applied to the Decimal instance number with a precision of one decimal place and the ROUND_DOWN rounding mode, which effectively truncates the value.
2. Using the to_integral_value Method
Another useful method provided by the Decimal class is to_integral_value. This method returns the nearest integer to the given decimal value, effectively truncating the decimal places.
The to_integral_value method allows developers to specify the rounding mode as well.
Here’s an example:
from decimal import Decimal, ROUND_DOWN
number = Decimal('3.14159')
truncated = number.to_integral_value(rounding=ROUND_DOWN) print(truncated)Output:
3In this example, the to_integral_value method is used with the ROUND_DOWN rounding mode, resulting in truncation.
3. Applying the Normalize Method
The normalize method of the Decimal class provides a way to adjust the exponent and scale of a decimal instance. By using this method, developers can effectively truncate the decimal places.
Consider the following example:
from decimal import Decimal
number = Decimal('3.14159')
truncated = number.normalize()
print(truncated)Output:
3.14159In this example, the normalize method is applied to the Decimal instance number, resulting in the same value without any decimal places.
Next, let’s look at ways you can truncate strings and lists in Python.
Truncation Techniques for Strings and Lists in Python
In this section, we’ll discuss various techniques for truncating strings and lists in Python functions. We’ll cover the following sub-sections: string truncate techniques and list truncation.
1. String Truncate Techniques
There are multiple ways to truncate a string in Python, including the use of str.format, slicing, and f-strings.
1) Using str.format: This method allows you to truncate a string by specifying a precision value. For example:
truncated_string = '{:.5}'.format('aaabbbccc')
print(truncated_string)
Output:
aaabb2) Using slicing: By using slice notation, you can select a substring of the original string. For example:
my_string = 'aaabbbccc'
truncated_string = my_string[:5]
print(truncated_string)
Output:
aaabb3) Using f-strings: With f-strings, the truncation can be performed inline within the string. For example:
my_string = 'aaabbbccc'
truncated_string = f'{my_string[:5]}'
print(truncated_string)
Output:
aaabb2. List Truncation
There are several ways to truncate lists in Python, such as slicing and using list comprehensions.
1) Using slicing: Slicing allows you to select a range of elements in a list. For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
truncated_list = my_list[:5]
print(truncated_list)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]2) Using list comprehensions: List comprehensions allow you to create a new list by iterating over an existing list and applying a condition or operation. For example, to truncate tuples in a list:
my_list = [('apple', 3), ('orange', 5), ('banana', 2)]
truncated_list = [(fruit, count) for fruit, count in my_list if count < 5]
print(truncated_list)
Output:
[('apple', 3), ('banana', 2)]
Now that we’ve covered the various techniques for truncating strings and lists using Python, let’s take a look at how you can do the same using libraries like NumPy and pandas.
How to Use NumPy and pandas to Truncate Values in Python
When it comes to numerical and data analysis in Python, the names ‘NumPy’ and ‘pandas’ undoubtedly resonate among developers. These powerful libraries have transformed the landscape of data manipulation by providing extensive functionality for array processing, data handling, and much more.
In this section, we’ll explore common ways to truncate elements in Python using NumPy and pandas DataFrames.
1. Truncation in Python Using NumPy
NumPy offers a simple, built-in function called trunc which allows you to truncate values to the nearest whole number.
The trunc function eliminates the fractional part of the input, returning only the integer.
import numpy as np
values = np.array([1.234, 5.678, 9.012])
truncated_values = np.trunc(values)
print(truncated_values)
Output:
array([1., 5., 9.])
Here are some key points about the trunc function:
It works element-wise, meaning it can truncate each element in an array or a list.
The data type (dtype) of the output array will be the same as the input array.
The function can be applied to different data structures, such as lists, tuples, or arrays, as long as the elements are numeric.
2. Using DataFrame and Loc for Truncation in Python
Pandas DataFrame is a powerful, flexible data structure for handling large, structured datasets. You can use the DataFrame.truncate() function to truncate a DataFrame based on the index.
To see a practical demonstration of how to load datasets in Python, watch this YouTube video:
Alternatively, you can use the loc property to filter rows or columns based on a specific condition.
import pandas as pd
data = {'A': [1.234, 5.678, 9.012], 'B': [4.567, 8.901, 2.345]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Truncating based on the index
truncated_df = df.truncate(before=1, after=2)
print(truncated_df)
Output:
A B
1 5.678 8.901
2 9.012 2.345
Using loc and a condition, we can achieve truncation based on values as well:
# Condition to truncate values in column 'A'
condition = (df['A'] < 6)
# Truncating DataFrame based on condition
truncated_df = df.loc[condition]
print(truncated_df)
Output:
A B
0 1.234 4.567
1 5.678 8.901
In this example, a boolean condition was used to filter out rows in the DataFrame. Depending on your use case, you can apply different conditions and operations using loc.
Let’s now look at the practical applications of truncation in Python.
3 Practical Applications of Truncation in Python
Understanding the concept of truncation in Python and its corresponding techniques is only half of the equation. The other half involves applying this knowledge effectively in practical scenarios.
In this section, we transition from theory to practice, illustrating how truncation can be used to optimize Python code in real-world applications.
Truncation is useful in various applications, some of which are:
1. Pengiraan kewangan : Apabila menggunakan mata wang, adalah perkara biasa untuk memotong nilai perpuluhan untuk mewakili wang sebenar yang hanya sen dipertimbangkan dan unit yang lebih kecil tidak berkaitan.
price = 49.987
truncated_price = int(price * 100) / 100
print(truncated_price)
Pengeluaran:
49.98
2. Pengagregatan data : Pemangkasan juga boleh digunakan untuk mengagregat data mengikut kriteria tertentu. Contohnya, mengagregat nilai min bacaan suhu harian berdasarkan nilai integer.
temperature_data = [22.3, 23.9, 24.8, 23.4, 22.7, 24.1, 24.6]
truncated_temperature = [int(temp) for temp in temperature_data]
mean_temperature = sum(truncated_temperature) / len(truncated_temperature)
print(mean_temperature)
Pengeluaran:
23.142857142857142
3. Menyusun elemen : Kadangkala, elemen perlu dipesan berdasarkan peraturan pemotongan tertentu. Ini boleh dicapai dengan menggunakan parameter utama dalam fungsi sorted() Python .
data = [4.8, 3.2, 2.9, 7.5, 6.1, 9.0, 1.5]
sorted_data = sorted(data, key=lambda x: int(x))
print(sorted_data)
Pengeluaran:
[1.5, 2.9, 3.2, 4.8, 6.1, 7.5, 9.0]
Aplikasi pemangkasan dunia sebenar ini menunjukkan ia tidak ternilai dalam pelbagai bidang, seperti analisis data dan pembelajaran mesin.
Yet, an important question arises: how do truncation techniques compare, and which method should you use for a given scenario? To answer this, our next section will dive into a comparative analysis of the various truncation methods we have discussed.
Comparing Truncation Methods in Python
To compare the different truncation methods in terms of performance and precision, let’s consider a large dataset and measure the execution time for each approach.
import random
import time
from decimal import Decimal, ROUND_DOWN
import math
# Generate a large dataset of floating-point values
data = [random.uniform(0, 1000) for _ in range(10**6)]
# Using int function
start_time = time.time()
truncated_int = [int(number) for number in data]
int_execution_time = time.time() - start_time
# Using math.trunc function
start_time = time.time()
truncated_math = [math.trunc(number) for number in data]
math_execution_time = time.time() - start_time
# Using decimal module
start_time = time.time()
truncated_decimal = [Decimal(str(number)).quantize(Decimal('1.'), rounding=ROUND_DOWN) for number in data]
decimal_execution_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Execution time using int function: {int_execution_time:.5f} seconds")
print(f"Execution time using math.trunc function: {math_execution_time:.5f} seconds")
print(f"Execution time using decimal module: {decimal_execution_time:.5f} seconds")
In this example, a dataset of one million random floating-point values between 0 and 1000 is generated. The execution time for each truncation method is measured using the time module. The decimal module approach converts each number to a Decimal instance before truncating to ensure accurate results.
By running the code, you can observe the execution times for each method and make a performance comparison.
Choosing the Appropriate Truncation Method
When it comes to truncating floating-point values in Python, choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific requirements of the application or use case.
Consider the following factors when deciding which method to use:
Precision: If precision is of utmost importance and you need fine control over decimal places, the decimal module provides the highest level of accuracy.
Performance: For simple truncation without the need for high precision, the int() function and math.trunc() function offer efficient solutions.
Rounding behavior: Depending on the desired rounding behavior, the decimal module allows you to specify various rounding modes, such as ROUND_DOWN, ROUND_UP, ROUND_HALF_UP, and more.
Compatibility: If you need to ensure compatibility with legacy code or systems that do not support the decimal module, the int() function or math.trunc function can be viable options.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the basics of truncating float values in Python is essential for accurate data manipulation and analysis. Python provides various methods and functions to truncate or round floating-point numbers based on specific requirements.
By using the built-in functions like math.trunc(), math.floor(), and math.ceil(), we can perform truncation operations effectively. These functions offer flexibility in handling positive and negative float values, allowing us to control the desired outcome.
Furthermore, the decimal module offers better control over rounding and precision, making it suitable for financial calculations or situations where accuracy is paramount.
As with any programming concept, practice and experimentation are key to mastering the art of truncating float values. Go ahead and apply these techniques in real-world scenarios and explore additional resources, such as Python documentation and community forums, to enhance your understanding and proficiency!
Apa Itu Diri Dalam Python: Contoh Dunia Sebenar
Anda akan belajar cara menyimpan dan memuatkan objek daripada fail .rds dalam R. Blog ini juga akan membincangkan cara mengimport objek dari R ke LuckyTemplates.
Dalam tutorial bahasa pengekodan DAX ini, pelajari cara menggunakan fungsi GENERATE dan cara menukar tajuk ukuran secara dinamik.
Tutorial ini akan merangkumi cara menggunakan teknik Visual Dinamik Berbilang Thread untuk mencipta cerapan daripada visualisasi data dinamik dalam laporan anda.
Dalam artikel ini, saya akan menjalankan konteks penapis. Konteks penapis ialah salah satu topik utama yang perlu dipelajari oleh mana-mana pengguna LuckyTemplates pada mulanya.
Saya ingin menunjukkan cara perkhidmatan dalam talian LuckyTemplates Apps boleh membantu dalam mengurus laporan dan cerapan berbeza yang dijana daripada pelbagai sumber.
Ketahui cara untuk menyelesaikan perubahan margin keuntungan anda menggunakan teknik seperti mengukur percabangan dan menggabungkan formula DAX dalam LuckyTemplates.
Tutorial ini akan membincangkan tentang idea pewujudan cache data dan cara ia mempengaruhi prestasi DAX dalam memberikan hasil.
Jika anda masih menggunakan Excel sehingga sekarang, maka inilah masa terbaik untuk mula menggunakan LuckyTemplates untuk keperluan pelaporan perniagaan anda.
Apakah LuckyTemplates Gateway? Semua yang Anda Perlu Tahu